News
01-27-2013
 New Books
New Books
Visit the Books Page on the homepage to See our Latest Releases
 New Books
New BooksVisit the Books Page on the homepage to See our Latest Releases
4 Scientifically Confirmed Cases of Particles Exceeding the Speed of Light
Some of these are exerpts from the March 2016 book: Wormhole Theories, Sunspot Activity and Remote Viewing Stocks
View Book Chapters

Read the first 3 Chapters Free
Keywords: Neutron star theory, Black hole theory, Light Speed theory, Tachyon theory, Wormhole theory, Exotic matter theory, Cosmic String theory, Quantum Gravity theory, Cesium Laser theory, Elementary particle ring and laser theory, Dirac antiparticle theory
It Shows Up Before the Button is Pressed
Einstein was not always right. He once stated that nothing physical could travel faster than the speed of light because it would mean travelling back in time. Work by Dr. Lijun Wang at the NEC research institute in Princeton demonstrated faster than light effects by transmitting a pulse of light towards a chamber that was filled with cesium gas. The experiment proved it moved through the chamber at up to 300 times the speed of light. This speed was so great, that before the pulse had a chance to completely enter the chamber, it appeared at the same instant 60 feet across the room. This was a period where it existed in two places at once. The theory also proved that time slows when objects exceed the speed of light. This is because the light beam races though the gas so quickly the leading edge of the pulse's peak ends up exiting before it enters. Due to the inerrant way light waves are able to be refracted, it makes this possible.
Refraction Helps Atoms Exceed the Speed of Light
By generating electromagnetic waves (microwaves) in his laboratory, Hertz showed they could be reflected and refracted just like light. Light behaves the same as electromagnetic radiation. Dr Wang's laser beams penetrated a group of boxed cesium atoms. It was only by tuning into the same resonance/wavelength of the energy levels in the atoms that he was able to create an effect known as "anomalous refractive index." By achieving refraction, it amplified the effect greatly allowing the waves to travel faster than the speed of light. The key depends on the frequencies occurring in the pulse and the medium through which it travels.
An obvious example of refraction is the effect sometimes seen when you see the same fish appearing to be in two different places in a fish tank. This occurs because the light coming from the fish to us changes direction when it leaves the tank. It can travel two different paths to get to our eyes. This changing of the rays of light (loosely called bending) when it passes through variations in matter (in most cases moisture) is called refraction.
This experiment does not threaten Einstein's theories. The causality principle states a cause must precede its effect. General relativity predicts a time delay that becomes progressively larger and larger as photons pass closer to the Sun due to the time dilation in the gravitational potential of the Sun. This could be why during solar eclipses there are accounts of gravitational time dilation.
Practical Uses: Encode the light waves with information, perhaps via a magnetic field and adjust the amplitude to extend its range up to 4 days out. Use it to receive information from the future.
Reference: L. J. WANG, A. KUZMICH & A. DOGARIU, Gain-assisted superluminal light propagation, Nature 2000, 406, 277 - 279. The paper was received by Nature May 11 and accepted for publication on June 26, 2000 URL:
https://www.eng.utoledo.edu/~jilu/papers_pdf/erasmo/wang_nature_superluminal00jul.pdf
Microwaves Travel Faster than the Speed of Light
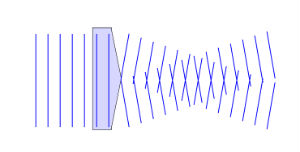
As just shown earlier, by generating electromagnetic waves (microwaves) in his laboratory, Hertz showed they could be reflected and refracted just like light. This gives them the ability to travel faster than the speed of light. Physicist Anedio Ranfagni and his team at the Italian National Research Council in Firenze were able to achieve superluminal velocities using microwaves. The experiment pumped beams of microwaves through a centimeters-wide ring. This was then reflected off of a curved mirror to create what is known as a "Bessel beam" of microwave light shown below:
Bessel beams consist of two planes of waves which intersect like an "X." Due to the unique structure of this geometric shape, as the point of intersecting waves converge, the waves are able to move much faster than the speed of the plane waves as they begin intersecting. Rafagni's team discovered the location at the intersecting location of the Bessel beam travelled 7% faster than the speed of light. The experiment does not violate Einstein's theory because the moving intersection is unable to carry a signal.
Practical Uses: Increase the amplitude of the microwave beam and turn it into a communications device. Send information along the microwave beam and use it to receive information from the future.
Reference: Comment on “Observation of Superluminal Behaviors in Wave Propagation”. N. P. Bigelow and C. R. Hagen. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 059401 – Published 16 July 2001. URL
http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.059401
FDTD Dispersion Revisited: Faster-Than-Light Propagation. John B. Schneider, Member, IEEE, and Christopher L. Wagner. IEEE MICROWAVE AND GUIDED WAVE LETTERS, VOL. 9, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 1999. URL
http://www.famakmakina.com/english/go2.php?go=http://www.eecs.wsu.edu/~schneidj/journal-papers/super-luminal.pdf
Cerenkov Radiation. Photons exceeding the speed of light
Cerenkov Radiation is an effect caused by radiation occurring in water due to the particles moving faster than the speed of light. Cerenkov radiation was discovered in 1934 by Pavel Cerenkov. Cerenkov radiation occurs most commonly in the core of nuclear reactors. Pavel observed that the water surrounding some radioactive substances showed a faint blue glow. The radiation is a byproduct of the particles travelling faster than light speed due to the density of the water. In order for Cerenkov radiation to occur the particles must be electrically charged.
Practical Uses: Use the time impeded photons to acclerate the rate at which radioactive decay occurs. Use this process to create a machine that processes radioactive waste, thus solving the problem of having to wait thousands of years for it to dissolve naturallly.
Reference
Cherenkov PA. Visible light from clear liquids under the action of gamma radiation.C.R. (DokI.) Acad. Sci. URSS 2:451-4, 1934.[Phyaico-Mathematicat Institute V.A. Stekiova. Academy of Science. Leningrad. USSR. URL
http://garfield.library.upenn.edu/classics1991/A1991GA09300001.pdf
Tachyons from Neutrinos
In a new paper that has passed peer review and been accepted by the journal Astroparticle Physics, Dr. Robert Ehrlich from George Mason University, claims that the neutrino is very likely a tachyon or faster-than-light particle. Neutrinos come from the sun as a product of nuclear fusion. They also exist in pulsars, which are rapidly rotating stars. Spinning neutron stars produces beams of longitudinal radiation that sweep across the line of sight, much like a lighthouse beam does for ships at sea. This occurs because a neutron star's magnetic field lines converge at its magnetic poles. This allows the charges to become focused into a narrow cone of non-thermal radiation which is then beamed outward. If the star happens to be aligned at the right angle towards earth, the beam will sweep past Earth, creating a brief flash of light. Could the rapidly rotating stars be creating faster than light particles?
If the Neutron star starts to rotate it becomes a Pulsar. Due to the rotation, pulsars produce very powerful beams of light. The pulsations of spinning neutron Stars are so accurate they are akin to atomic clocks on earth. The magnetic field of the star exerts a force on the charged particles, causing them to speed up. These charged particles then exert a reaction force on the magnetic field slowing it and the pulsar down and eventually the pulsar dies away. The spinning speed of a pulsar is greatly increased if the pulsar is near a binary system and the companion dumps gas onto the pulsar. This occurs due to the increased gas from the binary system falling onto it, much like greasing a wheel.
Neutron stars occur from the gravitational collapse of a massive star allowing them to have very high density, which creates extremely high gravity. One teaspoonful would weigh a billion tons! Time on these objects passes 30% slower. If someone was able to travel to such a star they would have a way to "travel" to the future, but not to the past.
Uses: Create a special telescope that can observe the tachyons emitted by neutron stars and then point the telescope at the future position of the star than use future position of the star to bounce a beam back towards earth resulting in a television image of the future.
Reference:
Tachyonic neutrinos and the neutrino masses. George Mason University. Accepted 22 September 2012. URL
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927650512001843
Cosmic Rays and Time Dilation
Cosmic rays are made up of Muons. Muons are particles produced when cosmic rays hit earth's atmosphere. They occur at an altitude of 15 km. Their average lifetime is approximately 0 = 2.210-6 s. In Newtonian mechanics, it simply means the muons move approximately c0 = 660 m before they decay, not allowing them to fully reach Earth. However, in fact a large fraction of muons actually reach the Earth. How can we explain this? Time dilation is the only explanation.
What is Time Dilation?
Time dilation is the difference of elapsed time between two events occurring when watched by observers as they are moving relative to each other. The Forbush Decrease may also be attributed to gravitational time dilation. Gravitational Time Dilation has also been found to occur during solar eclipses (A determination of the deflection of light by the Sun's gravitational field, from observations made at the total eclipse of 29 May 1919. F. W. Dyson, A.S. Eddington and C. Davidson 1920). Cosmic rays may also be showing effects of radiation pressure. Because light is one of the main forces influenced by radiation pressure due to its momentive force, cosmic rays also have a force of momentum which builds up over time. This radiation pressure caused by the momentum may be contributing to the gravitational time dilation effects.
Uses: Create a wristwatch sized device that generates a magnetic field to capture the muons and use it to slow down time on the outside of the bubble. This way you could walk around and everything would appear to have “stopped”, when in fact it is really moving very, very slowly.
References
The Speed and Lifetime of Cosmic Ray Muons. Lulu Liu (Partner: Pablo Solis). MIT Undergraduate. November 18, 2007. URL
http://web.mit.edu/lululiu/Public/pixx/not-pixx/muons.pdf
The Speed and Decay of Cosmic-Ray Muons: Experiments in the Relativistic Kinematics of the Universal Speed Limit and Time. Dilation. MIT Department of Physics. (Dated: October 17, 2014). URL
http://web.mit.edu/8.13/www/JLExperiments/JLExp14.pdf
How Solar Activity Affects the Speed of Earth's Rotation
During Dec 13, 2006, our sun sent a stream of particles and radiation towards Earth from a recent solar flare. During this event Purdue nuclear engineer Jere Jenkins was measuring the decay rate of manganese-54. Manganese-54 is a short-lived isotope that is used for medical diagnostics. He noticed the decay rate dropped slightly during this solar flare event. The drop in the decay rate started began showing up a day and a half before the solar flare actually took place. Based on recommendations from Dr. Peter Sturrock of Stanford, Jere Jenkins teamed up with Ephraim Fischbach to explore how solar activity affects the decay of radioactive materials.
In August of 2010 Purdue Professor Ephraim Fischbach, as well as scientists from Stanford discovered that the decay rates of radioactive materials occurred faster during summer and slower during the winter. The test was officially confirmed by teams at the US Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory. The test was also confirmed by the Federal Physical and Technical Institute in Germany. The study concluded that seasonal variations occurred in the decay rates of silicon-32 and radium-226. The researchers also discovered that decay rates varied every 33 days. This is the same period of time that roughly matches a full rotation of our sun (the rotation rate of our sun is 28 days). Could this mean that the reason radioactive substances decay faster during summer is because time is moving faster during summer, which is the time of year earth is furthest from our sun (its aphelion)?
During August of 1972, massive solar activity uncovered a discontinuous change in the length of day (LOD) immediately after the solar flare event. Calculations carried out by numerous observatories from around the world used UT2 time (Universal Time with the effects of the Chandler Wobble and seasonal variations removed). By calculating differences between Atomic Time (AT) and UT2 time, a disturbance was shown as the Earth's spin slowed down and the length of day increased.
John Gribbin noticed that during a solar storm in August 1972 that it created a "discontinuous change in the length of the day" caused by a change in earth's spin rate (J. Gribbin and R. A. Challinor. Science. 1971). The great solar storm of 1959 also contributed to an effect in the perception of time (A. Danjon. Informations de l' Observatoire de Paris. CR Acad. Sci. 1962) with effects resulting from changes in earth's rotation. (Revisiting a Possible Relationship between Solar Activity and Earth Rotation. R. Abarca del Rio and D. Gambis. September 2010). Solar activity also affects the speed at which earth's atmosphere travels around our earth. This can cause a delay to occur between solar activity and the speed of the atmosphere (D. Djurovic. January 1990).
When solar activity is lower, ionizing radiation in earth's stratosphere will increase due to more cosmic rays. This is because higher solar activity tends to pushes cosmic rays away from the Earth. The lower the solar activity, hence the more cosmic rays enter earth's atmosphere, creating more ionization (Rotation of the Earth, solar activity and cosmic ray intensity. T. Barlyaeva1 et al).
Researchers have studied the intensity of cosmic rays and their effect on the rotation of the earth (Rotation of the Earth, solar activity and cosmic ray intensity. 2 July 2014). Some scientists have theorized that the sun's heating or ionized atmosphere from higher cosmic rays acts as a heat engine due to earth's atmosphere becoming compressed. This can cause earth's rotation to speed up. A 1966 study confirmed there existed an influence in earth's atmosphere arising from solar activity (E. Schatzman. Interplanetary Torques. 1966). More recent studies notably Bourget et al (1992), revealed correlations between solar activity and the length of the day and studies done in 2003 (Abarca del Rio et al. 2003) and 2008 Winkelnkemper (2008) showed the length of day and atmospheric angular momentum were associated with changes from solar activity.
More in-depth studies have shown that Earth's mantle is responsible for the acceleration or de-acceleration effect according to variations in cosmic ray intensity caused by solar activity through the zonal winds. Because earth's mantle is so closely linked to seismic activity, recent studies have shown a link between that cosmic rays and earthquakes (Anderson, 1974). An excellent study published in February 2015 by M. Kovalyov and S. Kovalyov titled: On the relationship between cosmic rays, solar activity and powerful earthquakes, concluded the following: "cosmic rays play a much more prominent role that is currently believed; specifically that 1); cosmic ray intensity correlates with seismic activity on Earth with much accuracy than solar activity and 2); cosmic rays are influencing solar activity". As we covered earlier, during higher solar activity there will be less cosmic rays reaching earth because solar particles create a "shielding" effect, keeping the cosmic rays from completely reaching earth.
Read the first 3 Chapters Free
Thank You for visiting our site and reading our articles and new update. If this information has helped you or someone you know, please consider contributing to this site. Your contribution will ensure the continued publishing of unique and quality articles at no cost to all of our visitors and regular readers.